Ball Python morphs Charts
 Ball Pythons genetic charts Simple recessive, Co-dominant, Dominant:
Ball Pythons genetic charts Simple recessive, Co-dominant, Dominant:
The following charts are visual aides to help novice breeders understand genetics that they are interested in. The charts are based on law of averages actual results may vary.
Recessive
Homozygous: Means a pair of identical genes. These may be two identical normal genes or two identical mutant genes.
Heterozygous: Means a pair of non-identical alleles. Alleles are different versions of the same gene. The usual case is a normal allele paired with a changed (mutant) allele. An individual that is heterozygous for a recessive mutant gene look normal.
Examples of Simple recessive genes: Albino Ball Pythons, Clown Ball Pythons, Axanthic Ball Pythons, Piebald Ball Pythons and Hypomelanistic Ball Pythons.
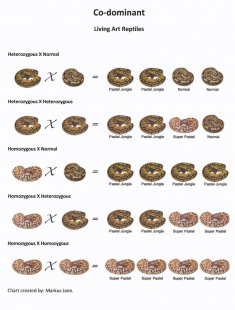
Co-Dominant
Homozygous: Super Pastel means a pair of identical genes. These may be two identical normal genes or two identical mutant genes.
Homozygous = Super Pastel
Heterozygous: Pastel means a pair of non identical alleles. Alleles are different versions of the same gene. The usual case is a normal allele paired with a changed (mutant) allele. An individual that is heterozygous for a Co-dominant mutant gene does not look normal and does not look like an individual that is homozygous for the Co-dominant mutant gene.
Examples of the Co-Dominant gene: Pastel Ball Pythons, Fire Ball Pythons, Yellow Belly Ball Pythons and Banana Ball Pythons.
Dominant
This is a visible mutation and appears when a single allele at a locus is different than the normal. A matched pair of the mutated allele will appear the same as the single. Dominants will carry the super form gene but it will not lookdifferent than the original dominant.
In dominant morphs the "Super"version or Homozygous snake is no different in appearance from the Heterozygous snake. the only way to determine the Homozygous individual is to breed and compare the consistency in the outcome.
Homozygous = Super Spider (will look like any other spider)
Heterozygous = Spider
Heterozygous: Means a pair of non-identical alleles. Alleles are different versions of the same gene. the usual case is a normal allele paired with a changed (mutant) allele. An individual that is heterozygous for a dominant mutant gene look like an individual that is homozygous for the dominant mutant gene.
Examples of dominant genes: Spider Ball Pythons, and Pinstripe Ball Pythons.
Best of luck,
Living Art Reptiles.
Source Information:
Markus Jane & Living Art Reptiles
Chart: Markus Jane.
- Disclaimer: please read before using this site. Any information posted on this web site is for general entertainment and educational purposes only, and should not be construed as medical advice, medical opinion, diagnosis or treatment. Any information provided by this web site is not a substitute for actual medical attention. Always promptly consult your licensed veterinary health-care professional for your pet's medical advice and treatment.
If you have any questions please contact us at:
Experience the Living Art!
Design © 1998-2014, Living Art Reptiles, LLC ® - Content © 1998-2014 Living Art Reptiles, LLC ®. Unless otherwise stated.
You might also like















 A contract is an agreement entered into voluntarily by two parties or more with the intention of creating a legal obligation, which may have elements in writing, though contracts can be made orally. The remedy for breach of contract can be "damages" or compensation of money. In equity, the remedy can be specific performance of the contract or...
A contract is an agreement entered into voluntarily by two parties or more with the intention of creating a legal obligation, which may have elements in writing, though contracts can be made orally. The remedy for breach of contract can be "damages" or compensation of money. In equity, the remedy can be specific performance of the contract or...